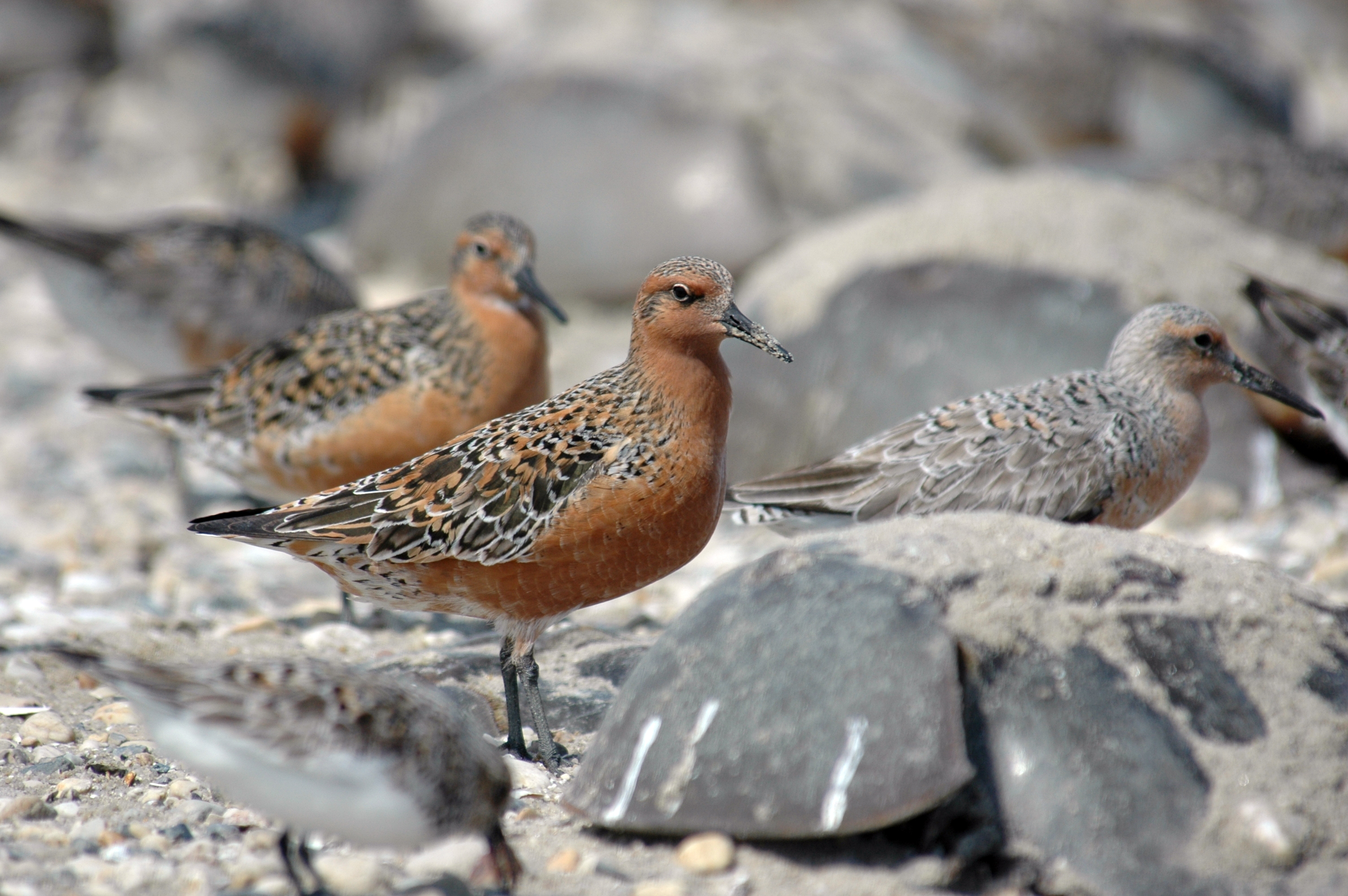
Red knot shorebirds make epic annual migrations, some logging up to 18,000 miles from the southern tip of South America to Canada and back, dropping down onto Delaware Bay beaches in May to gorge on horseshoe crab eggs.
That ancient pattern was disrupted by overharvesting of horseshoe crabs for commercial fishing bait in the 1990s. Biologists say neither the crab nor red knot populations have fully recovered yet.
Now, the prospect of dozens, perhaps hundreds of wind turbines spinning over waters on the East Coast outer continental shelf raises questions of how those structures may affect the red knot, considered a threatened species by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
Developers Atlantic Shores Offshore Wind LLC engaged one of the world’s top experts to find out.
“The birds jump off from Cape Cod, Brigantine, Stone Harbor,” said Larry Niles, ticking off coastal Massachusetts and New Jersey feeding grounds for the red knots. “We know the birds are going through the wind (power) areas.”
As the former chief of New Jersey’s Endangered and Non-Game Species Program, Niles started the Delaware Bay Shorebird Project, now in its 25th year of monitoring the migration. He’s now principal of Wildlife Restoration Partners, with years of experience assessing the health of red knots with other shorebirds and working on wind power studies.

Plans for 850-foot tall turbines might seem to present deadly barriers to the birds. But after years of tagging birds with ultra-lightweight tracking devices, researchers think the red knots over the ocean typically climb to cruising altitudes around 5,000 feet, said Niles.
The best fuel for that ascent is horseshoe crab eggs, tiny blue-green pellets that crabs lay on bay beach sands. In a few days voraciously feeding red knots can boost their body weight from 130 grams – about 4.5 ounces – up to 240 grams or 8.4 ounces, mostly new fat reserves to propel them onward.
“We model what the birds do while they’re migrating,” based on laborious downloading and interpretation of data from tracking transmitters, said Niles. Like human airliner pilots, in flight the birds are “assessing the strength and direction of the wind,” seeking the best airflow to speed their journey, said Niles.
The supply of crab eggs is critical to their success. The horseshoe crab bait business expanded in the 1990s to supply commercial eel and whelk trap fisheries. Shorebird counts on Delaware Bay beaches that were 90,000 in the late 1980s plummeted, and by the early 2000s Niles and environmental advocates convinced state wildlife agencies and the Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission to tighten catch limits.
Biologists who had measured up to 50,000 crab eggs per square yard of bay beaches saw those numbers drop to 5,000 before new regulations were set. The bird counts climbed back to around 30,000 in recent years, before dropping to 17,000 and then a new low point this spring of 6,880.
The 2020 migration season was affected by two early tropical storms on the East Coast in May that year, and persistent northerly winds this spring may have been a factor against the shorebirds, said Niles.
“This year the (horseshoe crab) spawn was on time, and I think it was good,” said Niles. “So I think we’re looking at a real decline” in the total numbers of the red knot population, he said.
That makes the Atlantic Shores project even more timely.
“It puts even greater value to the study,” said Niles. New satellite tags attached to red knots “will also give us really important conservation information,” with precise location data that will help U.S. and Canadian wildlife agencies map out habitat areas that should be saved for the birds, he said.
Paul Phifer, the permitting manager at Atlantic Shores, is familiar with shorebird conservation efforts from his time with the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service in the Northeast states.
“We got a petition to list the red knot (as an endangered species) years ago. We ultimately listed red knots as a threatened species in 2015,” said Phifer.
In his position now with the wind developers, Phifer talked to his old colleagues in the wildlife profession and realized the possibilities for a first study of wind power and shorebird migration.
“I knew Larry from working with him for all these years,” said Phifer. “What’s great now is the satellite tags are so advanced, and the birds are able to carry them.”
“The limited data we got last year shows they go really high” while migrating between South America, the U.S. East Coast and Canada, said Phifer. Niles will be in Brazil too to track one southern leg of the migration.
“We’re talking about a substantial long-term project,” said Phifer. Atlantic Shores is paying for all of the study costs – $95,000 last year and a projected $350,000 all told, with technical support from the Fish and Wildlife Service and New Jersey Audubon Society.
The shorebird study has not been a requirement of permitting from the federal Bureau of Ocean Energy Management. But Phifer says it is a wise long-term look at potential environmental impacts for the young U.S. offshore wind industry.
Environmental studies and precautions to avert bad effects on wildlife from developing offshore wind projects are critical, said Eric Stiles, executive director of the New Jersey Audubon Society.
At the same time, “if we don’t move ahead responsibly with offshore wind, a lot of these species are doomed” from climate change, he said.
Migratory flyways and potential bird losses from turbine rotor blades were studied when the Atlantic County Utilities Authority planned its five onshore turbines at the Atlantic City, N.J., sewage treatment plant. New Jersey Audubon experts assisted with that project, using modified small-boat radar to plot how birds passed near the site.
That three-year study counted 30 birds killed during that time, out of thousands onsite during those years, according to the agency in a 2015 report.
Since then, studies with Doppler radar have revealed more information about directions, altitudes and abundance of birds on the move, said Stiles.
With the Atlantic Shores study, “we’re really hoping it will set a precedent for having the industry move forward with government and academic partnerships,” said Stiles.







